Digital Dentistry: The CAD/CAM Revolution in Restorative Procedures
The landscape of restorative dentistry has been dramatically transformed by the advent of Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology. This digital revolution is reshaping how dental professionals approach restorations, offering unprecedented precision, efficiency, and patient satisfaction.
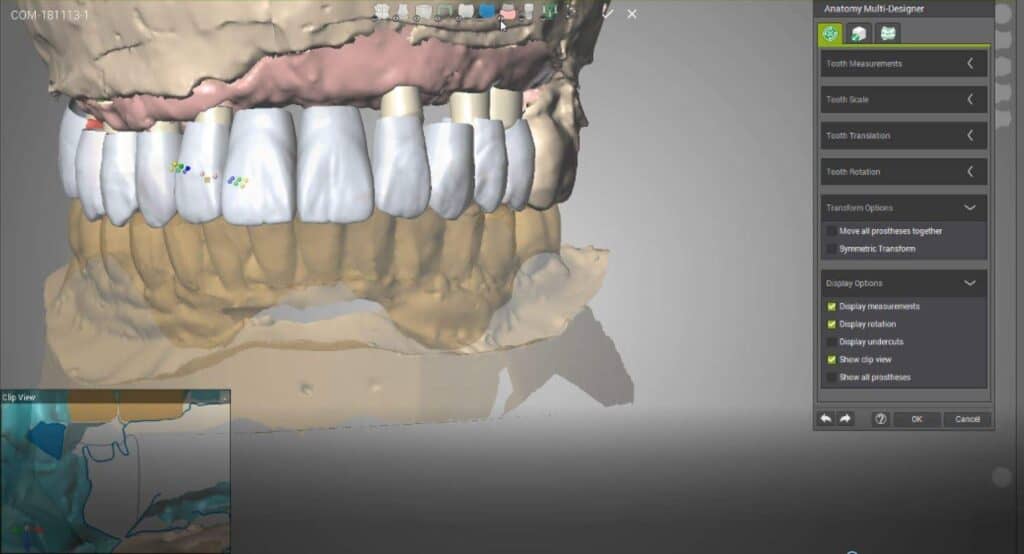
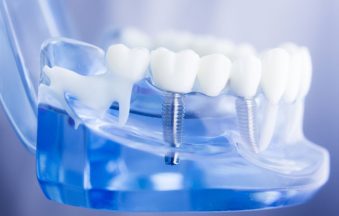
CAD/CAM systems have evolved from their initial introduction in the 1980s to become an integral part of modern dental practices. The technology allows for the digital design and fabrication of dental restorations, including crowns, bridges, veneers, and even full dentures. The process typically involves three main steps: digital scanning, computer-aided design, and computer-aided manufacturing.
Digital scanning has largely replaced traditional impression techniques in many practices. Intraoral scanners capture detailed 3D images of the patient’s dentition, eliminating the need for messy impression materials and improving patient comfort. These scans provide highly accurate digital models that serve as the foundation for designing restorations.
The design phase utilizes sophisticated software that allows dentists or dental technicians to create custom restorations with remarkable precision. These programs offer a range of tools for adjusting contours, occlusion, and aesthetics, ensuring that each restoration is tailored to the patient’s unique oral anatomy. The ability to visualize and modify designs in real-time has significantly enhanced the quality and fit of dental prosthetics.
The manufacturing process in CAD/CAM dentistry typically employs milling machines or 3D printers. Milling units can fabricate restorations from various materials, including ceramics, composites, and metals. The latest milling technologies can produce intricate designs with micron-level accuracy, resulting in restorations that fit better and require minimal adjustments.
3D printing, a more recent addition to the CAD/CAM arsenal, is gaining traction for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. This additive manufacturing technique is particularly useful for producing surgical guides, models, and even some types of prosthetics. As the technology advances, the range of printable dental materials continues to expand, offering new possibilities for restoration fabrication.
One of the most significant advantages of CAD/CAM technology is the ability to provide same-day restorations. In many cases, patients can receive their final crowns or veneers in a single appointment, eliminating the need for temporary restorations and multiple visits. This not only improves patient convenience but also reduces the risk of complications associated with temporary prosthetics.
The materials used in CAD/CAM restorations have also evolved alongside the technology. High-strength ceramics like zirconia and lithium disilicate can be milled to create durable, aesthetically pleasing restorations that rival natural teeth in appearance and function. These materials offer excellent longevity and are suitable for a wide range of clinical situations.
Digital dentistry has also facilitated improved communication between dentists, laboratories, and patients. Digital files can be easily shared, allowing for collaborative treatment planning and design modifications. Some systems even incorporate virtual articulation and smile design features, enabling patients to preview their restorations before fabrication.
While the benefits of CAD/CAM technology are numerous, it’s important to note that there is a learning curve associated with its implementation. Dental professionals must invest time in training and practice to fully leverage the capabilities of these systems. However, the long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and patient satisfaction often justify the initial investment.
Looking to the future, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into CAD/CAM systems promises to further streamline the design process and enhance outcomes. These technologies could potentially automate certain aspects of restoration design, allowing for even faster turnaround times and more predictable results.
For dental practices considering the adoption of CAD/CAM technology, it’s crucial to evaluate the various systems available and choose one that aligns with their specific needs and workflow. Factors such as ease of use, material compatibility, and integration with existing practice management software should be considered.
In conclusion, CAD/CAM technology represents a paradigm shift in restorative dentistry. By embracing these digital tools, dental professionals can offer their patients cutting-edge care characterized by precision, efficiency, and improved aesthetics. As the technology continues to advance, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly central role in shaping the future of dental practice.